Mia Shokry, Kimiyo Yamasaki, Ehab G. Daoud . J Mech Vent 2020; 1(1):24-26.
Cite
Shokry M, Yamasaki K, Daoud EG. Can you calculate the total respiratory, lung, and chest wall respiratory mechanics? J Mech Vent 2020; 1(1):24-25.
Metrics
Can you calculate the total respiratory, lung, and chest wall respiratory mechanics?
Abstract
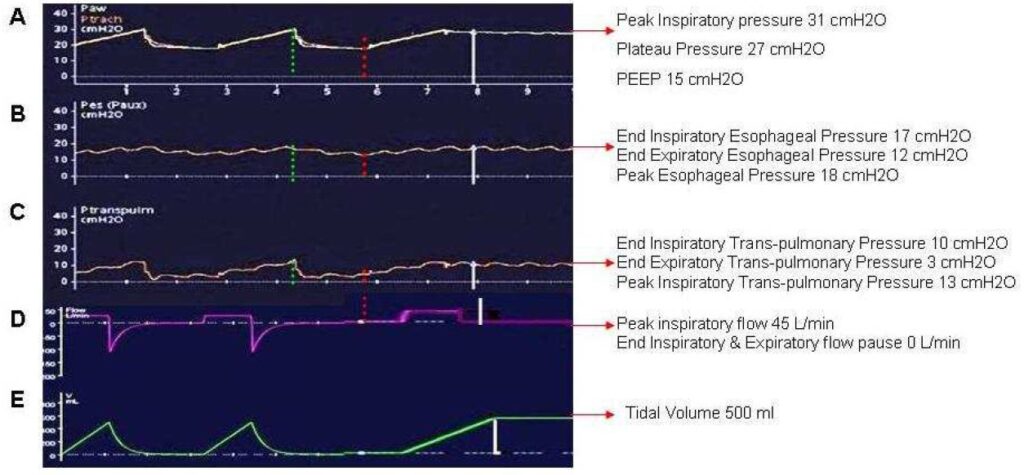
Figure: Waveforms for a patient undergoing mechanical ventilation with volume controlled mode. Tidal Volume of 500 ml, PEEP 15, Constant inspiratory flow of 45 l/min
A: Airway pressure in cmH2O, B: Esophageal pressure in cmH2O, C: Trans-pulmonary pressure in cmH2O, D: Flow in l/min, E: Tidal volume in ml
Red dashed horizontal line: values at end of expiratory occlusion maneuver, White solid horizontal line: values at end of inspiratory occlusion maneuver, Green dashed horizontal line: values during peak inspiratory pressure.
References
| 1. Iotti GA, Braschi, A. Measurements of respiratory mechanics during mechanical ventilation, Hamilton Medical Scientific Library, Rhazuns, Switzerland (1999) 66-82. Hamiltonmedical.nl. |
| 2. Hess DR. Respiratory mechanics in mechanically ventilated patients. Respir Care 2014; 59(11):1773- 1794. https://doi.org/10.4187/respcare.03410 PMid:25336536 |
| 3. The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 2000; 342:1301-1308. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200005043421801 PMid:10793162 |
| 4 Akoumianaki E, Maggiore SM, Valenza F, et al., The application of esophageal pressure measurement in patients with respiratory failure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2014; 189(5):520-531. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201312-2193CI PMid:24467647 |
| 5 Daoud EG, Katigbak R, Ottochian M. Accuracy of the Ventilator Automated Displayed Respiratory Mechanics in Passive and Active Breathing Conditions: A Bench Study. Respir Care 2019; https://doi.org/10.4187/respcare.06422 PMid:31311851 |
